microRNAs and their amazing potential
- Molecular regulators, enriched and stable in biofluids
- Tissue-specific markers
- Pathological processes alter expression profile
- Simply perfect biomarkers!
Biovendor introduces a new laboratory tool for differentiation of viral and bacterial respiratory tract infections (RTI) to reduce unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions.
The clinical significance of viral infections has been largely overlooked in the past. Viral infections are important determinants of adverse clinical outcomes, morbidity and mortality, particularly in critically ill and immunocompromised patients, neonates and young children. Distinguishing between bacterial and viral illnesses is important because it affects the choice of treatment and management strategies. It is particularly important in emergency patients in critical condition. Attention should also be paid to viral and bacterial co-infections, which can have similar clinical manifestations. If a patient has a bacterial infection but also an underlying viral infection that goes undiagnosed and untreated, this can increase the risk of complications and worsen the overall outcome. Examples include respiratory infections, fevers of unknown origin, pneumonia, and sepsis. An important subset of sepsis in children is “culture-negative sepsis,” which is often a viral infection. Recognition of viral sepsis is critical because it has implications for the appropriate use of antibacterial agents, infection control measures, and in some cases, specific, time-sensitive antiviral therapies. This is particularly urgent in high-risk children.
The MxA protein biomarker has the potential to provide important diagnostic information for urgent patients in various clinical situations where rapid differentiation between viral and bacterial infections is important for appropriate treatment and management. The high prevalence of combined viral-bacterial infections supports the use of MxA in combination with biomarkers of bacterial infection. Clinical studies show that the use of the MxA marker with either CRP and/or PCT has high clinical sensitivity and specificity to differentiate infectious aetiology and avoid inappropriate antibiotic therapy in viral infections.
Elevated MxA levels are more specific to viral infections and help differentiate viral infections from bacterial infections. MxA is useful in clinical practice to avoid unnecessary antibiotic treatments in viral infections. High MxA levels are found in presence of respiratory viruses such as Influenza A/B, Adenovirus, Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), SARS-CoV-2, Metapneumovirus, Parainfluenza Virus, Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV), or blood-transfered viruses such as Dengue virus, Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus (CCHF), Yellow Fever Virus, Chikungunya Virus, Rift Valley Fever Virus (RVFV).
MxA is used as a very early marker of viral diseases, as its concentration increases significantly due to viral infection as early as 1.2 hours and peaks after 16 hours. The clinical use of MxA has been described primarily in emergency departments and pediatrics, especially in patients with fever and symptoms of acute respiratory infection. Determination of MxA protein in combination with CRP could be a valuable test for early diagnosis of viral infection and differentiation of bacterial infection. In newborns or preterm newborns, the frequency of viral infections is 6-8 times more frequent over bacterial infections, and antibiotic treatment is overused substantially. Avoid unnecessary antibiotic treatments substantially reduces risks of immunity damage or later autoimmunity disorders development in the patient group. Decision limits vary depending on the used analytical method and the biological material being investigated. The combination of MxA with CRP values offers a high negative predictive value (99%), effectively identifying individuals who do not require antibiotic treatment.
High throughput CLIA MxA kit (ask us: quotes@bio-connect.nl)
Most sensitive 96well Human MxA ELISA kit
Easy to perform POCT / MxA Lateral Flow Test (ask us: quotes@bio-connect.nl)
The gold nanoparticle conjugate-based lateral flow assay for MxA uses a pair of specific monoclonal antibodies to bind MxA protein from the sample. The assay provides quantitative results when the appropriate reader is used to read the signal. The assay provides quantitative results if Bi-Reader® is used to read out the signal.
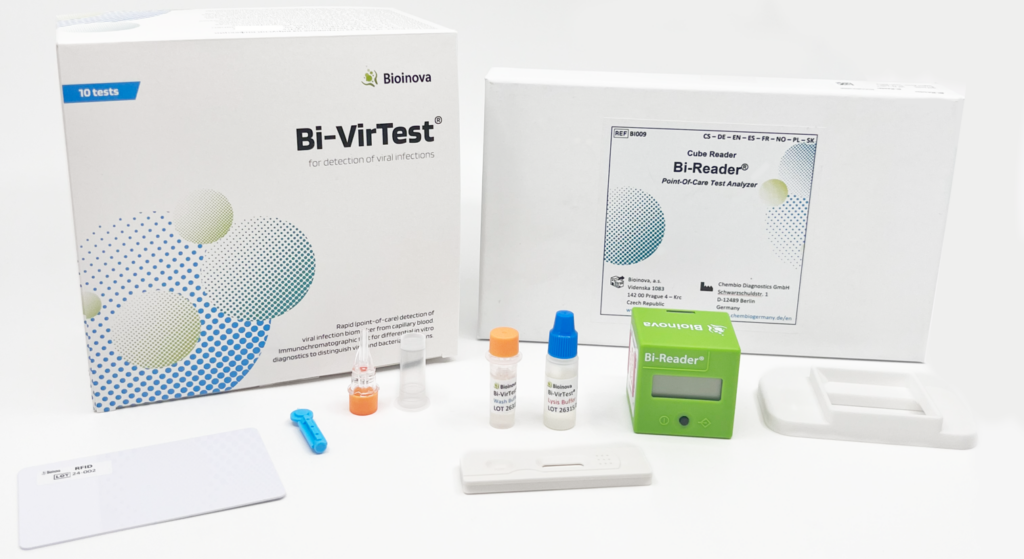
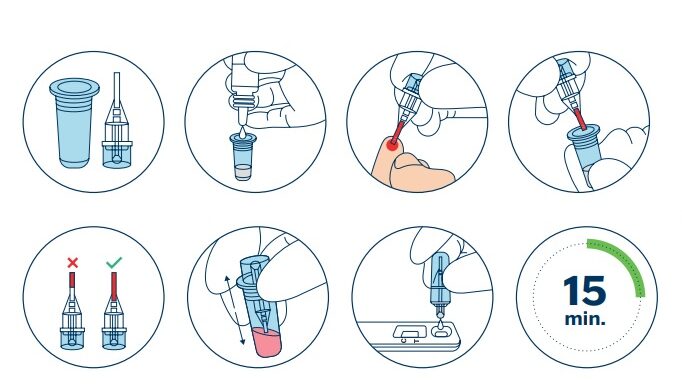
Find here more about the MxA POCT test here:
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.