Advancing Diagnostic Solutions for Myeloid Malignancies
Myeloid malignancies are clonal diseases of hematopoietic stem or progenitor cells. Myeloid malignant diseases comprise and acute (acute myeloid leukemia) stages.
Confidence in your lab’s results is easy with objective NGS data and straightforward, flexible applications.
In the fast-paced world of cancer research, having confidence in your lab’s results is crucial. The ability to use objective NGS data combined with user-friendly, flexible applications has become an essential tool for researchers like you. LymphoTrack NGS Assays deliver that power to your fingertips, unlocking potential and achieving better outcomes.
Say goodbye to uncertainty and hello to precise and impactful results. With confidence in your lab’s outcomes, the possibilities are endless.
Invivoscribe’s LymphoTrack® Assays are designed to be flexible so you can run routine or custom-designed experiments on existing, in-house NGS systems to produce results you can be confident in.
Featuring innovative approaches for measurable residual disease (MRD) detection using next-generation sequencing (NGS).
Comparison of Measurable Residual Disease in Pediatric B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using Multiparametric Flow Cytometry and Next-Generation – Hwang et al. Ann Lab Med. 2024.
Optimizing Molecular Minimal Residual Disease Analysis in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia – Starza et al. Cancers. 2023.
Quantification of Measurable Residual Disease Detection Q18 by Next-Generation Sequencing Based Clonality Testing in B-Cell and Plasma Cell Neoplasms – Lui et al. J Molec Diag. 2024.
Minimal/Measurable Residual Disease (MRD) Monitoring in Patients with Lymphoid Neoplasms by High-Throughput Sequencing of the T-Cell Receptor – Tung et al. J Molec Diag. 2023
Optimizing Molecular Minimal Residual Disease Analysis in Adult ALL – Starza et al. Leukemia. 2023;15,374.
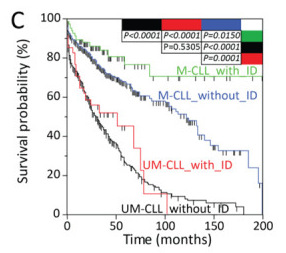
Over 20 years ago, two pioneering publications identified somatic mutations in IGHV genes as a significant prognostic marker in CLL, in which mutated IGHV correlated with improved progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).1,2
Recent research3 indicates that “some CLL may exhibit evidence of IGHV clonal evolution through the introduction of new mutations, in a process known as intraclonal diversification (ID).”
1. Damle RN, et al. (1999) Blood. 94(6):1840-7.
2. Hamblin TJ, et al. (1999) Blood. 94(6):1848-54.
3. Vit, F. et al. (2023) HemaSphere. 7(Suppl e939603e):8 Aug. 2023
Clonal Characterization and Somatic Hypermutation Assessment by Next-Generation Sequencing in CLL/SLL: A Detailed Description of the Technical Performance, Clinical Utility, and Platform Comparison – Petrova-Drus, K et al. (2023) Journal of Molecular Diagnostics. 25(6):352-366.
Up to 6.5 years (median 4 years) of follow-up of first-line ibrutinib in patients with CLL/SLL and high-risk genomic features: integrated analysis of two phase 3 studies – Burger, JA et al. (2022) Leukemia & Lymphoma. 63(6):1375-1386.
Immunoglobulin Variable Heavy Chain Somatic Hypermutation Testing in a Patient with Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma – Saadalla, AM et al. (2021) The Journal of Applied Laboratory Medicine. 6(6):1665–1670.
NGS Analysis of Clonality and Minimal Residual Disease in a Patient with Concurrent Richter’s Transformation and CLL/SLL – Burger, JA et al. (2021) Case Reports in Hematology. 2021(9740281):10.
Evaluation of Somatic Hypermutation Status in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) in the Era of Next Generation Sequencing – Gupta, SK et al. (2020) Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 8:357.

Next-generation sequencing of immunoglobulin genes in lymphoid malignancies
Presented by: Dr. Rena Xian, M.D., M.S. from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine

NGS-based Clinical Assessment of B- and T-cell Clonality and MRD Determination
Presented by: Dr. Alejandro Medina Herrera from University Hospital of Salamanca & Dr. Carolina Terragna from IRCCS – University Hospital of Bologna

Development and Implementation of an Automated and Highly Accurate Reporting Process for NGS-based Clonality Testing
Presented by: Sean T. Glenn, PhD – Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.