Cortical layers
Cortical layer markers provide a useful tool for studying the development, functional neuroanatomy and pathology of the cerebral cortex.
Integrins, receptors for the extracellular matrix
Integrins are a family of transmembrane receptor proteins, connecting the cy-toskeleton with the extracellular matrix (ECM). Integrins bind to ECM glycopro-teins including collagens, fibronectins, laminins, and a number of cellular receptors. In addition, integrins function as signal transducers. Importantly, different integrins activate differential intracellular signaling pathways that control biological and cellular functions including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, cell differentiation, and apoptosis [1].
Integrins are formed by two noncovalent-ly bound alpha and beta subunits. There are 18 alpha and 8 beta subunits, forming at least 24 distinct integrin heterodimers. Each heterodimer consists of a large extracellular domain, binding proteins in the extracellular environment, a single-membrane-spanning transmembrane domain, and a generally small intracellular cytoplasmic tail domain, which forms links with the cytoskeletal elements [2].
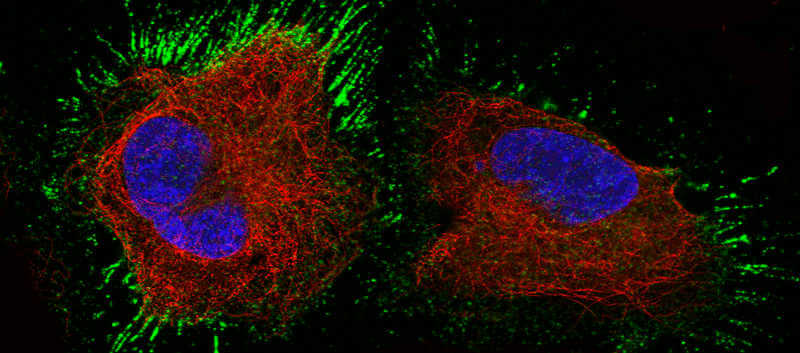
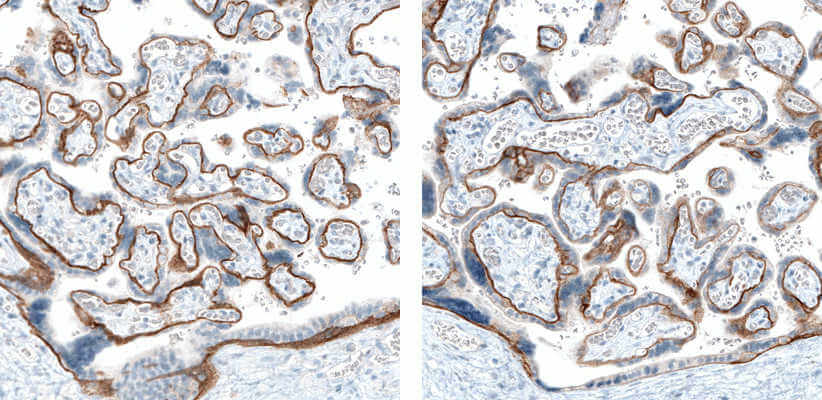
The specificity of integrin binding to ECM components including laminins, collagens, and fibronectin depends on the extracellular domains of the alpha and beta integrin subunits. Integrins a1b1, a2b1, a10b1, and a11b1 represent the primary collagen receptors [2]. Integrins a5b1, a8b1, aIIbb3 and the avb integrins are the major fibronectin receptors that bind in an RGD-dependent manner [3]. Finally, integrins a3b1, a6b1, a6b4 and a7b1 are the major laminin receptors [4].
A selection of Atlas Antibodies offering against specific integrin subunits is summarized in the tables below.
| Anti-ITGB1/CD29 (HPA059297) |
| Anti-ITGB2 (HPA016894) |
| Anti-ITGB3 (AMAb91470) |
| Anti-ITGB4 (AMAb91454) |
| Anti-ITGB5 (HPA001820) |
| Anti-ITGB6 (HPA023626) |
| Anti-ITGB8 (AMAb91467) |
Are you looking for specific products, alternatives, documentation or need assistance?
How can we help?We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.