High quality biomarker kits from Biomedica
Trusted and widely cited ELISA assays for cytokines and biomarkers in bone metabolism, cardiovascular and renal diseases, cancer, and oxidative stress.
Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) is a new potential biomarker for IgA Nephropathy (IgAN) research.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a progressive loss in kidney function and it affects 1 in 10 people around the world. Major causes of CKD are type 2 diabetic nephropathy, polycystic kidney disease and chronic glomerulonephritis. IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is the most common type of primary chronic glomerulonephritis. Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) has been reported as a critical effector molecule in the pathogenesis and progression of IgAN and measuring Gd-IgA1 can replace biopsy.
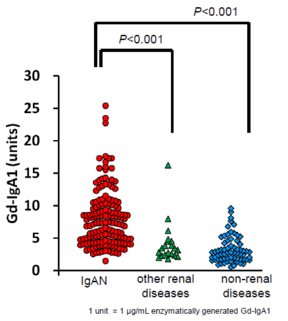
The measuring system using snail (helix aspersa; HAA) lectin has been used in past numerous studies to detect serum levels of Gd-IgA1 in patients with IgAN. However, instability of glycan-recognizing activity, development of alternative measuring is desired.
IBL Japan’s ELISA kit, Gd-IgA1 (Galactose-deficient IgA1) Assay Kit (27600), using monoclonal antibody (KM55) specifically recognizes galactose-deficient hinge sequence of human Gd-IgA1, is a lectin non-dependent measuring system that can quantitatively measure Gd-IgA1 in human serum, EDTA-Plasma and urine.
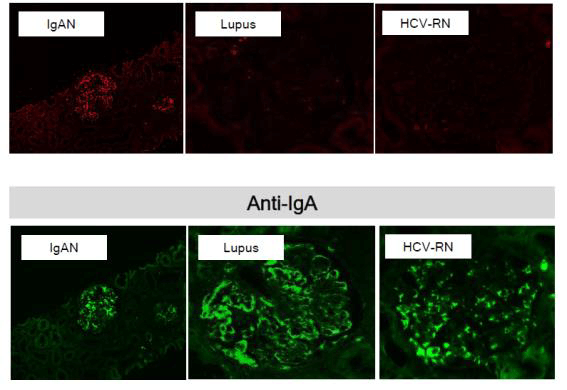
IBL’s monoclonal antibody, Anti-Human Gd-IgA1(KM55) Rat IgG MoAb (10777), can detect Gd-IgA1 in tissue by IHC technique differently from the feature of HAA lectin and it has been revealed that Gd-IgA1 specifically exists in glomeruli of the patients of IgAN.
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.