DNA extraction kits from BioChain
Fast, accurate, and easy to use, BioChain’s DNA purification kits make life in the lab easier and enhance success
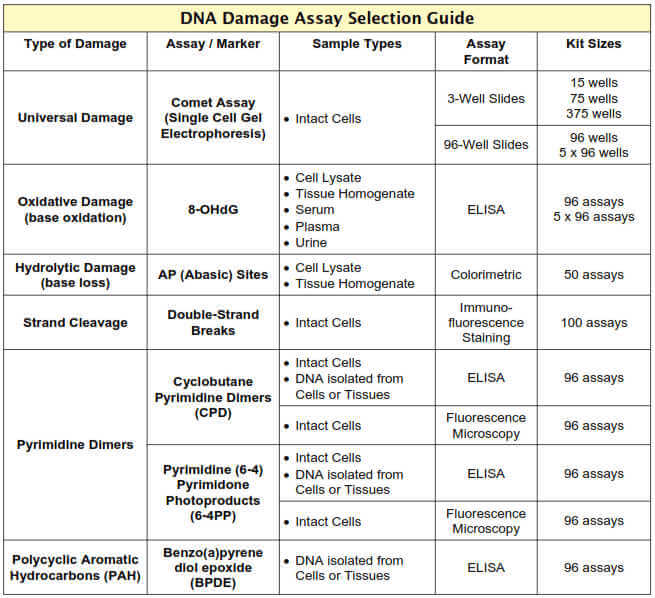
Easily measure distinct types of nucleic acid damage in various assay formats
DNA is arguably one of the most biologically significant targets of cellular stress. DNA may be damaged by a variety of endogenous and exogenous sources, and the damage may take various forms:
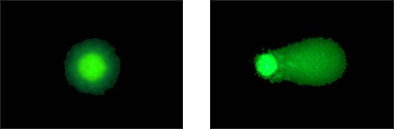
The Comet Assay is a well-published method to detect various types of DNA damage in intact cells by electrophoresis. Damaged DNA is easily distinguished from healthy DNA by light microscopy; the damaged DNA moves farther when current is applied, creating a “comet” shape (see below).
8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) is the most common marker for oxidative DNA damage and can be measured in virtually any species. It is formed and enhanced most often by chemical carcinogens.
The OxiSelect™ Oxidative DNA Damage ELISA provides a highly sensitive method for measuring 8OHdG formation. Detect as little as 100 pg/mL in DNA isolated from urine, serum, cells and tissues.
Like its DNA counterpart 8-OHdG above, 8-OHG (8-hydroxyguanosine) is the most common marker for oxidative RNA damage.
The OxiSelect™ Oxidative RNA Damage ELISA has a detection limit of 300 pg/mL and is suitable for use with cells, tissues, serum, urine or cerebrospinal fluid.
Loss of DNA bases can be particularly mutagenic, and if left unrepaired these AP (apurinic /apyrimidinic) sites can inhibit transcription. The OxiSelect™ DNA Damage Quantitation Kit (AP sites) provides a highly sensitive method for quantitation of AP sites. Quantify as few as 4-40 AP sites per 105 bp of DNA in tissue or cell lysates.
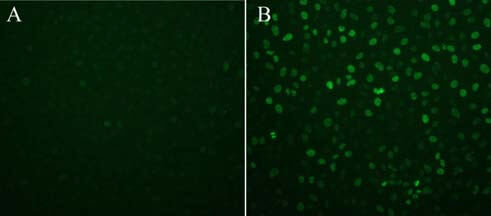
Double-strand breaks (DSB) in DNA are among the most dangerous types of DNA damage. One of the first responses to DSBs in mammalian cells is the phosphorylation of the Ser139 residue of a histone variant, H2AX, which occurs within seconds at the site of the damage. This phosphorylation causes chromatin condensation and appears to play an important role in recruitment of repair factors.
The OxiSelect™ DNA Double-Strand Break Staining Kit detects DSBs in cultured cells.
Absorption of ultraviolet radiation can damage DNA by the formation of pyrimidine dimers. The two main forms of pyrimine dimers are cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD) and pyrimidine (6-4) pyrimidone photoproducts (6-4PP).
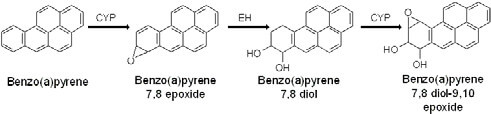
Benzo(a)pyrene diol epoxide (BPDE) is a mutagen that may create adducts with DNA as well as proteins. It is a derived from benzo(a)pyrene which is polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), a family of chemical carcinogens commonly found in environmental pollution.
For more information about all protein oxidation & nitration assays to accurately measure oxidative and nitrative protein damage, Lipid peroxidation assays to quantify stable by-products of lipid peroxidation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) assays to measure ROS with high sensitivity in intact cells, cell lystaes or blood samples and all antioxidant assays for quantifying antioxidant capacity or specific antioxidant enzymes, please contact our technical support.
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.