Neuroinflammation monoclonal antibodies
Atlas Antibodies offers a wide range of neuroinflammation markers. Their antibodies are affinity-purified, reproducible, and selective for their target proteins through an enhanced validation process.
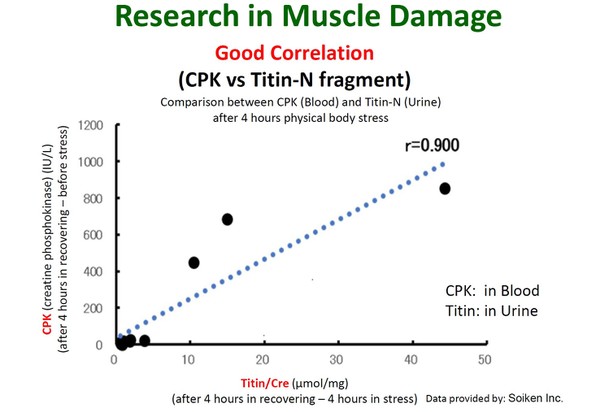
Titin N-fragment is a useful tool in research of sport medicine (muscle damage), ALS, NAFLD, cardiac disease, sarcopenia and frailty etc.
Titin (connectin) is a protein that consists of 34,350 amino-acid (3,816kDa) and specifically expresses in a cross-striated muscle. Titin has been known as the largest protein among of existing proteins in a living body. It has been researched in the field of muscular damages such as sports medicine, cardiac disease, NAFLD, sarcopenia and frailty etc.
A group of researchers, headed by prof. Masahisa Katsuno, MD. PhD., at department of Neurology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine (Nagoya, Japan) have conducted a study of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in which they enrolled 70 ALS patients and 43 healthy controls (HC) and assessed urinary Titin N-fragment, urinary neurotrophin receptor p75 extracellular domain (p75ECD), serum neurofilament light chain (NfL) and motor functions to evaluate their relevance as a marker of disease progression and prognosis of ALS.
As a result, they revealed that urinary Titin N-fragment levels normalised with Cr (titin/Cr) were significantly high in ALS patients (ALS, 27.2 pmol/mg/dL vs HC, 5.8 pmol/mg/dL; p<0.001) and associated with the scores of motor functions ALSFRS-R (r=-0.422, p<0.001) and patients with high Titin N-fragment showed poor prognosis.
For measurement of urinary Titin N-fragment level, #27900 Human Titn N-fragment Assay Kit – IBL is used in this report.
Yamada S, Hashizume A, Hijikata Y, et al. Ratio of urinary N-terminal titin fragment to urinary creatinine is a novel biomarker for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2021;92(10):1072-1079.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by rapid progression of motor neuron loss, which causes systemic atrophy of skeletal muscles and decline of motor function, leading to dysphagia and paralysis of respiratory muscles. Until today 2 drugs for ALS have been approved in Japan, yet they have limited beneficial effects. Also, sensitive and non-invasive markers that can be used for disease monitoring and disease prediction weren’t established.
In this report, urinary Titin N-fragment and p75ECD were associated with ALSFRS-R. These findings suggest that urinary Titin N-fragment, as well as urinary p75ECD, reflects ALS severity. Furthermore, a Cox proportional hazards model demonstrated that the high urinary level of urinary Titin N-fragment was a survival predictor in patients with ALS. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors showed that the urinary Titin N-fragment and serum NfL were independent factors for poor prognosis.
Thus it is concluded that urinary Titin N-fragment can be in combination with these markers useful to estimate disease progression and disease prognosis of ALS.
The antibodies Anti-Titin-N (53A1) Mouse IgG MoAb (10423) and Anti-Titin-N (144A2) Mouse IgG MoAb (10425) specifically react to human Titin N-Fragment and can be used in ELISA application.
All products are supplied by Bio-Connect Diagnostics in the Benelux.
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.