Primary Cancer Culture System
A complete defined and animal-component free cell culture solution designed for the selective culture of malignant cells derived from primary tumors or patient-derived xenografts.
Powerful tools for in vivo CSC drug discovery and basic cancer research
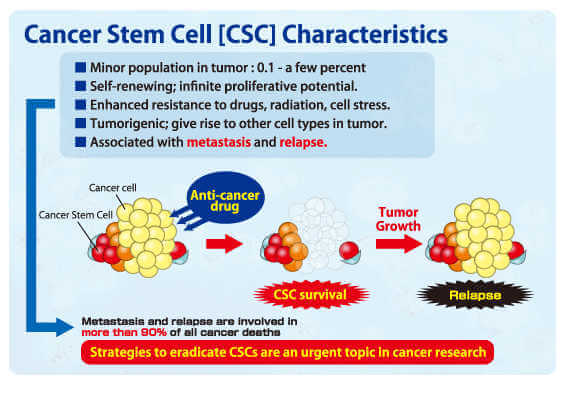
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are defined as a small, self-renewing cell population within a tumor that can give rise to all other tumor cell types found within that tumor. It is currently accepted by many that failure to eradicate CSC populations severely limits the ultimate effectiveness of many current cancer therapies. Thus, CSCs are considered to be critical targets for an important new generation of anti-cancer strategies. However, as CSCs make up only a very small, and diffuse, population of total tumor mass, detailed functional analyses critical to the development of such strategies has been difficult. Recently however, the ability to enrich and characterize CSC from several tumor types based on the expression of cell surface marker phenotypes is leading to significant progress in defining the nature and roles of CSCs in tumor formation, tumor plasticity, tumor recurrence, and tumor metastasis.
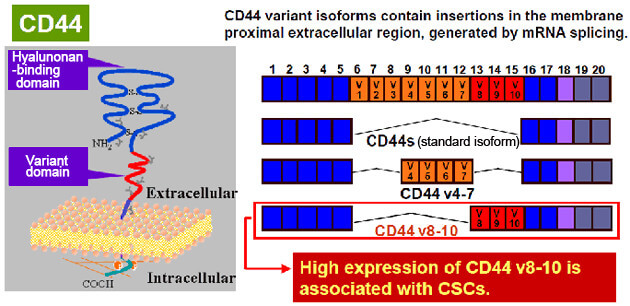
CD44 is a single-pass type I transmembrane protein and functions as a cellular adhesion molecule for hyaluronic acid, a major component of the extracellular matrix. CD44 exists in numerous isoforms generated through mRNA splicing. Whereas the standard isoform of CD44 (CD44 s) is expressed predominantly in hematopoietic cells and normal epithelial cell subsets, CD44v (variant) isoforms contain insertions in the membrane-proximal extracellular region and are highly expressed in epithelial-type carcinomas. Moreover, CD44 is reported as cell surface marker for cancer stem cells (CSCs) derived from solid tumors including breast, prostate, colon, head and neck and pancreatic cancer. Expression of CD44, especially variant isoforms (CD44 v8-10), also contribute to reactive oxygen species (ROS) defense by playing a role in controlling glutathione (GSH) synthesis, the primary intracellular antioxidant. CD44 v8-10 interacts with and stabilizes xCT, a subunit of the cystine-glutamate transporter xc(-), and thereby promotes cystine uptake to enhance GSH synthesis. The ability to avoid the consequences of exposure to high levels of ROS is required for cancer cell survival and propagation in vivo. Thus, enhanced resistance to ROS is thought to be an important contributing factor to CSC survival, and a driver of tumor growth, metastasis, and chemoresistance.
| Type of cancer | CSC markers |
|---|---|
| Colon cancer | CD44+ CD133+ |
| Breast cancer | CD44+ CD24-/low |
| Gastric cancer | CD44+ |
| Pancreatic cancer | CD44+ CD24+ ESA+ |
| Hepatic cancer | CD133+ |
| Prostate cancer | CD44+ |
| Metastatic melanoma | CD20+ |
| Head and neck cancer | CD44+ |
| Brain tumor | CD133+ |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | CD34+ CD38- |
CD44 is a single-pass type I transmembrane protein and functions as a cellular adhesion molecule for hyaluronic acid, a major component of the extracellular matrix.
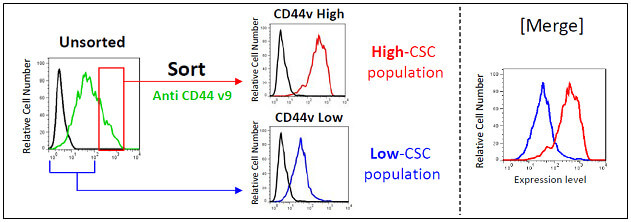
These highly specific CD44v monoclonal antibodies are highly recommended for measuring CD44v expression by flow cytometry and for enrichment of CSC populations by cell sorting.
♦ Examples of preparative CSC enrichment from human cancer cell lines using anti-CD44 v9 antibody RV3 (Cat. No. CAC-LKG-M001).
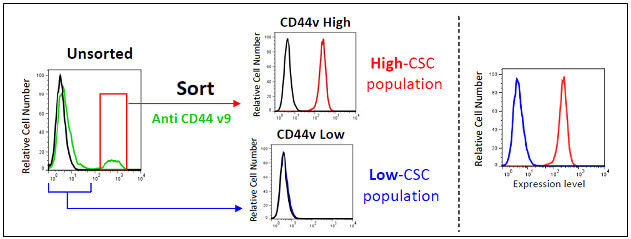
♦ Application Example 1.
In vitro evaluation of CSCs by “sphere formation assay”
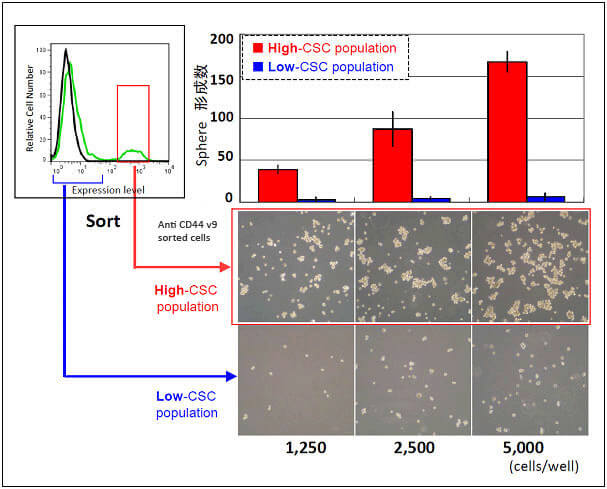
In vitro sphere formation assays are a type of colony formation assay used to evaluate the clonogenic potential of CSCs and other stem cells. and can be used to evaluate the effects of drugs on this potential. The figure below compares the sphere formation ability of CD44 v9-High and CD44 v9-Low cell populations sorted from a human prostate cancer cell line (PC-3) using anti-human CD44 v9 antibody RV3 (Cat. No. CAC-LKG-M001). The increased number of spheres observed with CD44 v9-High selected cells (CSC enriched) allows for more accurate assessment of the effects of inhibitory drugs and other treatments on CSC sphere formation.
♦ Application Example 2.
In vivo evaluation of CSCs by “lung metastasis assay”
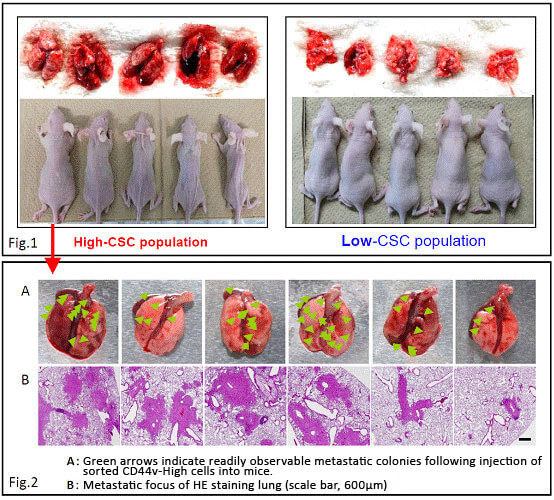
Lung metastasis assays, in which tumorigenic cells are injected intravenously into a test animal, offer a convenient opportunity to assess the inhibitory effects of compounds or other treatment on ability of CSC to colonize an unrelated tissue site. However, few lung foci are observed using non-enriched CSC containing populations, making it difficult to obtain meaningful data. Positive selection for high CD44v expression can greatly increase the number of observed foci, greatly increasing the utility of this assay for biological and drug discovery research.
Lung metastasis assay study comparing the ability of CD44 v9-High and CD44 v9-Low expressing cell populations sorted from the human pancreatic cancer cell line AsPC-1 to colonize mouse lung.
| Anti CD44 Antigen v9 mAb (Clone RV3) (CAC-LKG-M001) |
| Anti CD44 Antigen v9 mAb (Clone RV3) (CAC-LKG-M003) |
| Anti CD44 Antigen v10-e16 mAb (Clone RM1) (CAC-LKG-M002) |
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.