Incretin-Based Research: A New Era in Diabetes and Weight Management
AdipoGen‘s incretin-based reagents, including GLP-1 and GIP agonists, are revolutionizing the research for diabetes and weight management.
Assay Genie: Immunometabolism is a growing, multi-disciplinary field of research aiming at deciphering the dynamic cellular and molecular mechanisms that interweave metabolic and immunological processes together.
Tumour cells often create an immunosuppressive environment, hindering the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack malignant cells. This suppression is partly due to metabolic alterations within the tumour microenvironment that affect immune cell function. For instance, cancer cells may consume excessive glucose, depriving effector T cells of the energy needed for their activity.
Therapeutic strategies targeting these metabolic pathways aim to restore immune function. By inhibiting specific metabolic processes in tumour cells or modulating the metabolism of immune cells, it’s possible to enhance the body’s natural anti-tumour response.
Autoimmune diseases arise when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, often due to an imbalance between effector and regulatory T cells. Metabolic pathways play a crucial role in this balance. Effector T cells rely on glycolysis for rapid energy, while regulatory T cells depend on oxidative phosphorylation.
Modulating these metabolic pathways offers a potential therapeutic approach. By promoting the metabolic processes that favour regulatory T cell function, it may be possible to suppress the aberrant immune responses characteristic of autoimmune diseases.
In summary, targeting immunometabolism presents a novel avenue for therapeutic development in both oncology and autoimmune conditions. By focusing on the metabolic requirements of immune cells, researchers can devise strategies to either bolster immune responses against tumours or dampen them in the context of autoimmunity.
The following experimental methods provide valuable insights into the metabolic pathways of immune cells and their adaptive changes in both health and disease. These assays can be used independently or in combination to gain a comprehensive understanding of immune cell metabolism.
The uptake of glucose is an essential early step in meeting cellular energy demands, making its measurement a useful indicator of immune cell metabolism. To assess glucose transport, cells are incubated with a traceable glucose variant. Traditionally, this was done using radio-labeled glucose (such as 2-deoxy-D-[3H] glucose), but fluorescent glucose analogs like 2-NBDG or 6-NBDG are now preferred due to their ease of use. After incubation, the amount of glucose analog absorbed by the cells is quantified using scintillation counting or flow cytometry, with results normalized to cell number.
| Assay | Code | Read-out | Sensitivity | Sample type | Pack size |
| 1,5-Anhydroglucitol Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) | BN00908 | Fluorometric | N/A | Adherent/Suspension | 50 Assays |
| 2-NBDG Glucose Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) | BN00906 | Fluorometric | N/A | Adherent/Suspension | 50 Assays |
| Glucose Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) | BN00905 | Fluorometric | N/A | Adherent/Suspension | 50 Assays |
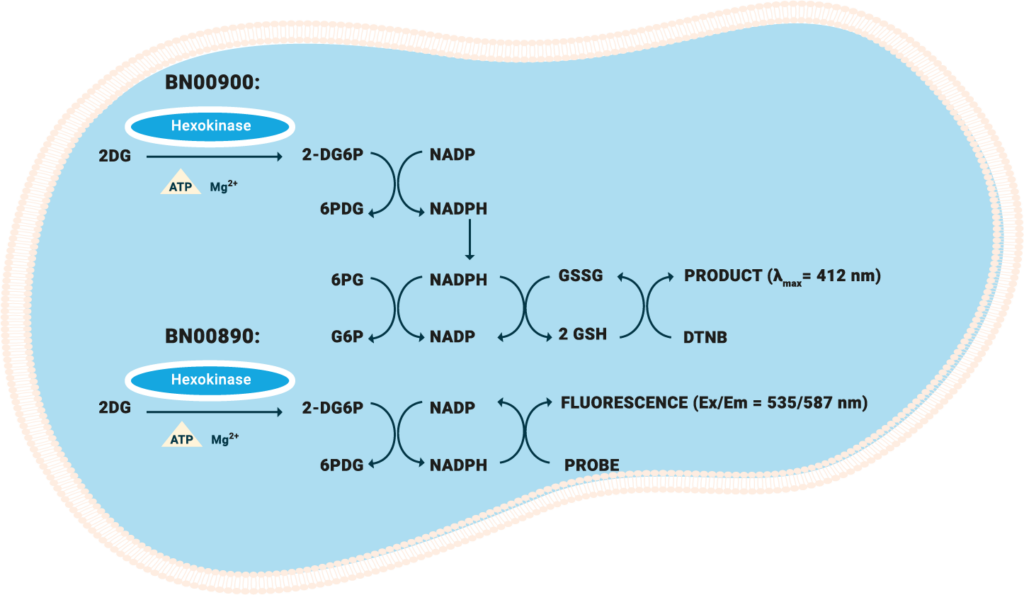
| Glucose Uptake Colorimetric Assay Kit | BN00900 | Colorimetric | 10 pmol | Adherent/Suspension | 100 Assays |
| Glucose Uptake Fluorometric Assay Kit | BN00890 | Fluorometric | 1000 pmol | Adherent/Suspension | 100 Assays |
| Direct Glucose Uptake Assay Kit | BN01098 | Fluorometric | 5pmol | Adherent/Suspension | 50 Assays |
In human immune cells, glucose transporters—primarily members of the Glut family—can be detected on the cell surface or intracellularly using flow cytometry with fluorochrome-labeled antibodies. However, careful validation of antibody specificity and staining efficiency is necessary. Additionally, changes in glucose transporter expression should always be evaluated alongside glucose uptake or other metabolic markers to ensure accurate interpretations.
A holistic view of cellular metabolism can be obtained by analyzing mitochondrial oxygen consumption and glycolysis. One of the most effective approaches is using live-cell metabolic assay platforms, such as Agilent’s Seahorse XF Bioanalyzers™, which measure the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) in real time. These assays, performed in multi-well plates, allow for the addition of metabolic modulators to observe their effects on mitochondrial function, helping researchers identify mechanisms underlying metabolic dysregulation.
Advancements in mass spectrometry have enabled the development of highly sensitive metabolic assays. By incorporating isotopically labeled tracers, researchers can examine the movement and utilization of specific metabolites ex vivo, providing detailed insights into immune cell metabolism.
A wide range of chemical inhibitors targeting different metabolic pathways can be used alongside these assays to study disrupted metabolic processes in immune cells. These inhibitors help determine how metabolic alterations influence immune cell function and overall immune responses. The table below provides a non-exhaustive list of small molecules that can be used to probe metabolic reprogramming events in immune cells.
| Name | Target | Metabolic Outcome |
| 2-deoxyglucose | Hexokinase | ↓ glycolysis |
| 3-bromopyruvate | Hexokinase | ↓ glycolysis |
| Ritonavir | Glucose transporter 1 | ↓ glycolysis |
| Dichloroacetate | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase | ↓ glycolysis |
| FX11 | Lactate dehydrogenase | ↓ glycolysis |
| 4-CIN | Monocarboxylate transporters | ↓ glycolysis |
| DASA and TEPP46 | Pyruvate kinase M2 | ↓ HIF1α |
| C75 | Fatty acid synthase | ↓ fatty acid synthesis |
| Etomoxir | Carnitine palmitoyl transferase I | ↓ fatty acid oxidation |
| AICAR | AMP kinase | ↑ fatty acid oxidation |
| Cerulenin | Fatty acid synthase | ↓ fatty acid synthesis |
As our understanding of the intricate link between T cell metabolism and key processes like survival, differentiation, and function expands, it becomes increasingly clear that immune system dynamics are tightly connected to overall metabolic regulation. While targeting metabolic pathways to modulate immune responses holds significant therapeutic potential, findings from preclinical and clinical studies have often been inconsistent. Further research is needed to clarify these effects across different immune cell populations and within diverse microenvironments.
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.